In medical institutions, many patients have questions when visiting a doctor: Why do I need to undergo an enhanced CT scan after having a regular CT? What is the significance of an enhanced CT? Is it necessary?
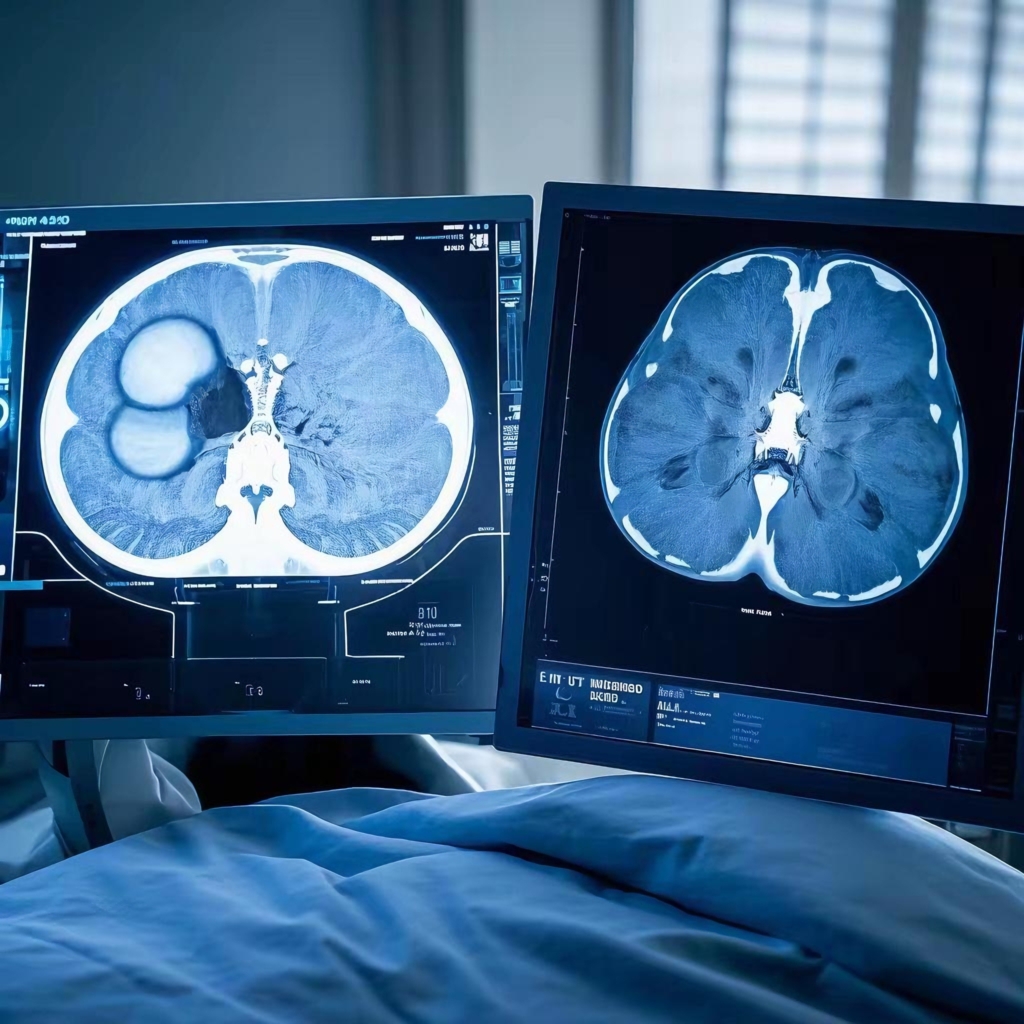
The key difference between a regular CT and an enhanced CT is that the latter requires the injection of a contrast agent into the body. This contrast agent enhances the imaging effect, making the distinction between diseased tissue and surrounding normal tissue much clearer.
The significance of an enhanced CT lies in three main aspects:
1. Reduced Missed Detection Rate: Regular CT scans have limitations in identifying lesions. Enhanced CT, through dynamic scanning, can detect lesions that are easily overlooked, thereby significantly reducing the rate of missed diagnoses.
2. Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Lesions: Regular CT scans have limited ability to characterize lesions. Enhanced CT, however, can greatly improve the qualitative assessment of lesions by analyzing the presence, degree, and pattern of enhancement. This allows for more accurate diagnoses, especially in typical cases.
3. Accurate Tumor Staging: Enhanced CT can precisely determine the location and extent of tumor invasion. This information is crucial for planning surgical procedures and evaluating treatment outcomes based on changes in blood supply within the lesion before and after treatment.
Enhanced CT is particularly important for the diagnosis of various conditions, including suspected brain tumors, cerebrovascular malformations, inflammation, lung tumors, mediastinal tumors, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, systemic peripheral vascular diseases, as well as tumors in the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, bladder, prostate, uterus, ovaries, and gastrointestinal tract.
The primary mechanism of enhanced CT is to increase the density difference between the lesion tissue and adjacent normal tissue, thereby improving the visibility of the lesion. This increase in density is referred to as “enhancement.” It occurs because the lesion tissue often has abundant blood vessels, slow blood flow, or a disrupted blood-brain barrier, causing the iodine-based contrast agent to accumulate and enhance the pathological tissue. Enhanced scanning can thus reflect the nature of the lesion tissue.
Enhanced CT offers several key benefits:
1. Improved Detection of Isodense and Small Tumors: It clarifies the specific number, size, and morphology of lesions, providing more detailed information.
2. Enhanced Qualitative Diagnosis: By observing the blood supply of the tumor, surrounding blood vessels, and the degree of lymph node involvement, enhanced CT improves the ability to differentiate between benign and malignant tumors.
3. Tumor Staging: Enhanced CT is particularly useful for analyzing the degree of enhancement, especially in liver cancer lesions. This helps to better distinguish cancerous lesions in the liver and provides a basis for clinical treatment decisions.
4. Differentiation of Blood Vessels and Enlarged Lymph Nodes: Enhanced CT is highly effective in distinguishing between blood vessels and enlarged lymph nodes.
5. High Diagnostic Accuracy: Enhanced CT is especially valuable in clarifying the nature of liver space-occupying lesions and the malignancy of chest tumors. In the differential diagnosis of liver lesions, it excels in distinguishing between liver cysts, hemangiomas, nodular hyperplasia, cirrhosis, and malignant tumors.
Disclaimer: The above pictures are from the Internet. If they infringe on anyone’s patent, please contact us in time to delete them.